Entropy and Second Law of Thermodynamics
Entropy and Second Law of Thermodynamics: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Entropy, Factors Affecting Entropy, Entropy Change for Phase Transition & Entropy Change for Ideal Gases etc.
Important Questions on Entropy and Second Law of Thermodynamics
For vaporization of water at 1 atmospheric pressure, the values of respectively. The temperature when Gibbs energy change for this transformation will be zero, is:
The values of for the reaction, respectively. This reaction will be spontaneous at
Considering entropy (S) as a thermodynamic parameter, the criterion for the spontaneity of any process is:
Unit of entropy is:
of an ideal gas at temperature is expanded reversibly from to . Find the entropy change.
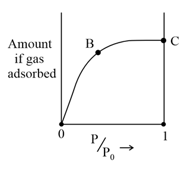
The adsorption of a gas at the boiling point of the gas follows the isotherm shown in the figure. Identify the correct thermodynamic properties at point
A heat engine absorbs heat at temperature and heat at temperature . Work done by the engine is . This data
For which of the following processes, is negative?
The molar heat capacity () of is at . The change in entropy associated with cooling of of vapour from at constant pressure will be : ( = deuterium, Atomic mass = )
The enthalpy of vaporization of water at is . Its entropy of vaporization would be
The unit of is
What does entropy measure?
A container is divided into two compartments by a removable partition as shown below:
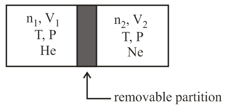
In the first compartment, moles of ideal gas He is present in a volume In the second compartment, moles of ideal gas is present in a volume The temperature and pressure in both the compartments are and respectively. Assuming is the gas constant, the total change in entropy upon removing the partition when the gases mix irreversibly is:
The change in entropy at equilibrium is
The enthalpy of vaporization of water at is . Its entropy of vaporization would be
will be highest for
In which of the following processes, entropy of the system increases?
) Temperature of a crystalline solid is raised from to .
) Liquid crystallizing to solid.
)
) Vaporization of a liquid.
Among the following processes, for which process the change in entropy is negative?
Elemental sulfur is formed by the reaction of with oxygen at :
If and . Then is :
Elemental sulfur is formed by the reaction of with oxygen at
If and . Then is :
